docker学习之Containers_02
1、创建一个目录,并在这个目录下创建一个文件:Dockerfile,拷贝下面的代码到这个文件中。# Use an official Python runtime as a parent imageFROM python:2.7-slim# Set the working directory to /appWORKDIR /app# Copy the current directory contents into the container at /appADD . /app# Install any needed packages specified in requirements.txtRUN pip install --trusted-host pypi.python.org -r requirements.txt# Make port 80 available to the world outside this containerEXPOSE 80# Define environment variableENV NAME World# Run app.py when the container launchesCMD ["python", "app.py"]

2、继续创建两个文件:requirements.txt和app.py,并把他们和Dockerfile放在同一个文件目录中,复制的时候注意,最好使用gedit命令,vi粘贴的时候不准确。(1)requirements.txt:FlaskRedis
3、(2)app.py:from flask import Flaskfrom redis import Redis, RedisErrorimport osimport socket# Connect to Redisredis = Redis(host="redis", db=0, socket_connect_timeout=2, socket_timeout=2)app = Flask(__name__)@app.route("/")def hello(): try: visits = redis.incr("counter") except RedisError: visits = "<i>cannot connect to Redis, counter disabled</i>" html = "<h3>Hello {name}!</h3>" \ "<b>Hostname:</b> {hostname}<br/>" \ "<b>Visits:</b> {visits}" return html.format(name=os.getenv("NAME", "world"), hostname=socket.gethostname(), visits=visits)if __name__ == "__main__": app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=80)

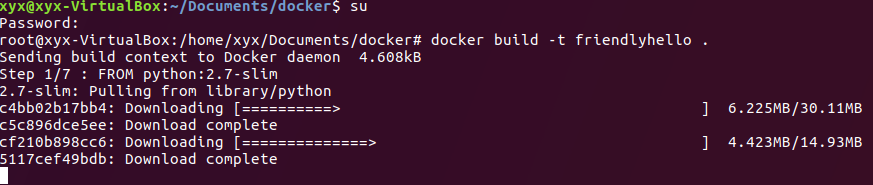
4、Build the app:编译应用。这个命令将会创建镜像,并存储到Docker仓库中。注意后面的".",直接拷贝此段命令,注意切换到root权限,会下载一些文件,最终会看到success。docker build -t friendlyhello .
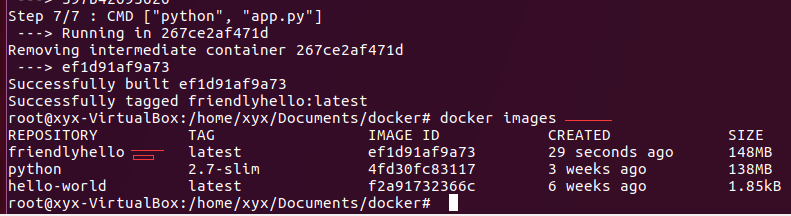
5、查看Docker镜像:docker images
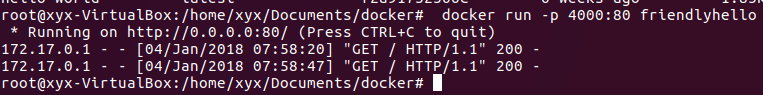
6、Run the app:启动app,配置本机的端口4000映射到容器端口80。其相当于服务器,不要关闭,可以使用Ctrl+C关闭docker run -p 4000:80 friendlyhello

7、重新打开一个终端:访问容器,每访问一次服务端就会有一行输出。curl http://localhost:4000


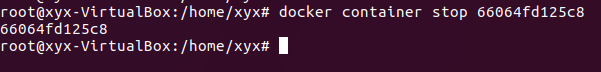
8、查看container ID,查看实时运行的容器:docker container ls
9、使用container ID 关闭,此时会发现第一个终端自动退出了,和Ctrl+c一样。命令:docker container stop 66064fd125c8